Running an x86 Yocto Linux image under QEMU KVM
Host OS preparation (VM manager host OS)
Steps:
1.Enable KVM on the host machine
2. Enable on host OS vhost-net virtio networking accelerator to mitigate overhead on QEMU virtualization environment.
Load vhost-net module on KVM Host.
[root@dlp ~]#modprobe vhost_net [root@dlp ~]#lsmod | grep vhost
The result of running the commands should be similar to the following:
vhost_net 24241 0 macvtap 7867 1 vhost_net tun16825 3 vhost_net
Note
- You need log out then log in the non-root user to take the effect
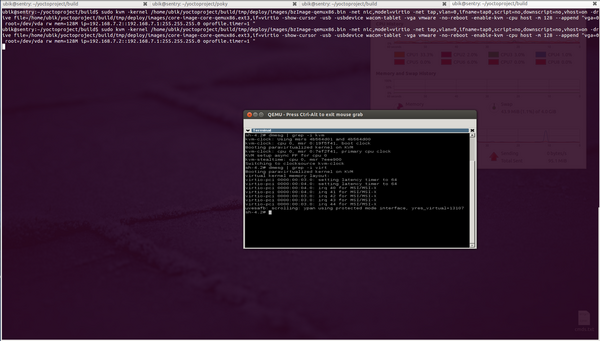
3. Start the VM using the line below:
ubik@sentry:~/yoctoproject/build$ sudo kvm -kernel /home/ubik/yoctoproject/build/tmp/deploy/images/bzImage-qemux86.bin -net nic,model=virtio -net \
tap,vlan=0,ifname=tap0,script=no,downscript=no,vhost=on -drive file=/home/ubik/yoctoproject/build/tmp/deploy/images/core-image-core-qemux86.ext3,if=virtio \
-show-cursor -usb - usbdevice wacom-tablet -vga vmware -no-reboot -enable-kvm -cpu host -m 128 --append "vga=0 root=/dev/vda rw mem=128M \
ip=192.168.7.2::192.168.7.1:255.255.255.0 oprofile.timer=1 "
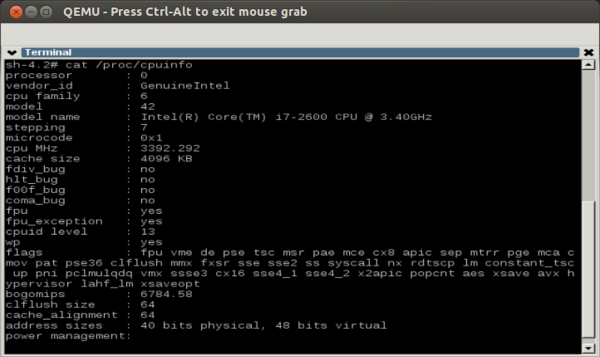
This is an example of running a virtualized Yocto image, with KVM active, cpu host features exported in the Yocto VM, paravirtualization enabled, and using virtio interfaces for disk access and networking. On a machine equipped with a Core i7 2600 (3.4GHz, 4 cores, 8 threads)/8 GB RAM/Intel SSD G3 120GB qemux86 Yocto Linux boots in around 7 seconds for a core-image-x11. The same image boots in 20 seconds without virtualization optimizations and feels slower in usage.
Guest OS preparation
The following kernel configs needs to be enabled for Yocto Linux guest OS:
[...] CONFIG_PARAVIRT_GUEST=y CONFIG_KVM_CLOCK=y CONFIG_KVM_GUEST=y CONFIG_PARAVIRT=y CONFIG_PARAVIRT_CLOCK=y CONFIG_VIRTIO_MMIO=y [..]
Screenshots example: