Vmstat
From Yocto Project
Jump to navigationJump to search
System monitoring with vmstat
The following results were obtained based on data collected using vmstat, a tool that reports a system's virtual memory statistics.
In order to reproduce the output shown in section 2, one should:
- Fetch upstream code from the core-image-minimal recipes
$ git clone git://git.yoctoproject.org/poky $ cd poky/ $ source oe-init-build-env $ echo -e 'DL_DIR = "/home/user/poky/downloads"' > conf/auto.conf $ bitbake core-image-minimal -c fetchall
- Start vmstat in a new terminal (set a 2 sec interval)
$ vmstat 2 > vmstat-output.raw
- On the terminal from the first step, launch bitbake, making sure no network activity will be done
$ echo -e 'BB_NO_NETWORK = "1"' >> conf/auto.conf $ bitbake core-image-minimal
- Once bitbake finishes, Ctrl+D the vmstat command to stop it
Vmstat output
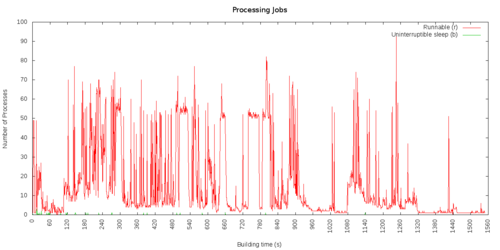
Processing jobs
Procs
r: The number of runnable processes (running or waiting for run time).
b: The number of processes in uninterruptible sleep.
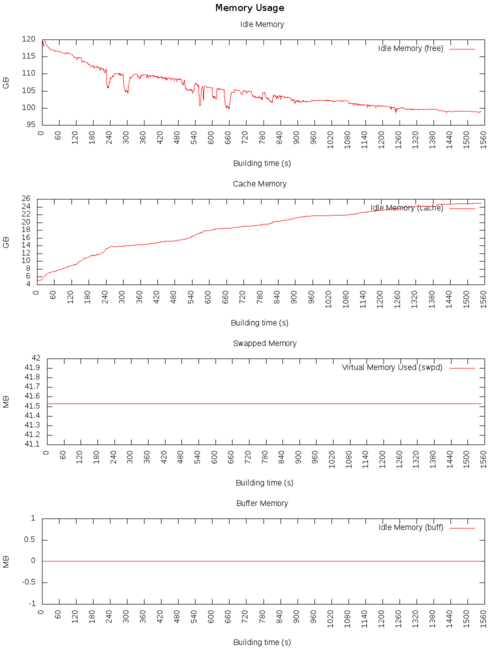
Memory usage
Memory
swpd: the amount of virtual memory used.
free: the amount of idle memory.
buff: the amount of memory used as buffers.
cache: the amount of memory used as cache.
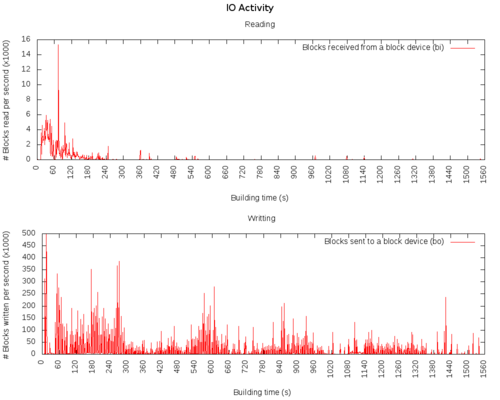
IO activity
IO
bi: Blocks received from a block device (blocks/s).
bo: Blocks sent to a block device (blocks/s).
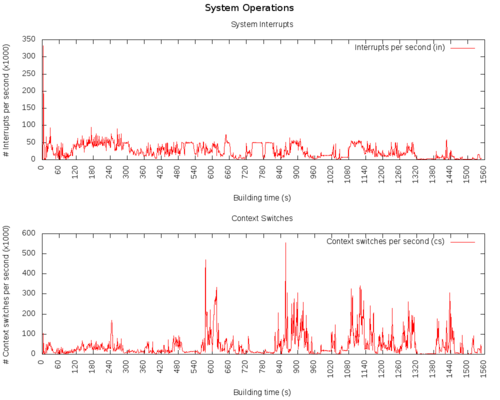
System operations
System
in: The number of interrupts per second, including the clock.
cs: The number of context switches per second.
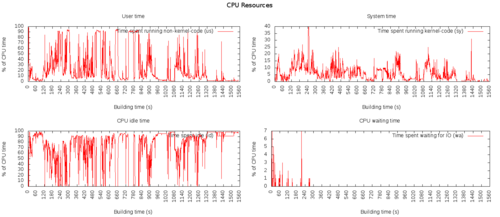
CPU performance
CPU
These are percentages of total CPU time.
us: Time spent running non-kernel code. (user time, including nice time)
sy: Time spent running kernel code. (system time)
id: Time spent idle. Prior to Linux 2.5.41, this includes IO-wait time.
wa: Time spent waiting for IO. Prior to Linux 2.5.41, included in idle.
st: Time stolen from a virtual machine. Prior to Linux 2.6.11, unknown.