Running an x86 Yocto Linux image under QEMU KVM: Difference between revisions
Emma.ciobanu (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Emma.ciobanu (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Host OS preparation (VM manager host OS) == | == Host OS preparation (VM manager host OS) == | ||
1. [https://wiki.yoctoproject.org/wiki/How_to_enable_KVM_for_Poky_qemu Enable KVM] on the host machine | 1.[https://wiki.yoctoproject.org/wiki/How_to_enable_KVM_for_Poky_qemu Enable KVM] on the host machine | ||
2. Enable vhost-net to mitigate overhead on QEMU virtualization environment. | 2. Enable on host OS vhost-net virtio networking accelerator to mitigate overhead on QEMU virtualization environment. | ||
<br/>Load vhost-net module on KVM Host. | <br/>Load vhost-net module on KVM Host. | ||
[root@dlp ~]#modprobe vhost_net | [root@dlp ~]#modprobe vhost_net | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
3. Start the VM using the line below: | 3. Start the VM using the line below: | ||
ubik@sentry:~/yoctoproject/build$ sudo kvm -kernel /home/ubik/yoctoproject/build/tmp/deploy/images/bzImage-qemux86.bin -net nic,model=virtio -net tap,vlan=0,ifname=tap0,script=no,downscript=no,vhost=on -drive file=/home/ubik/yoctoproject/build/tmp/deploy/images/core-image-core-qemux86.ext3,if=virtio -show-cursor -usb -usbdevice wacom-tablet -vga vmware -no-reboot -enable-kvm -cpu host -m 128 --append "vga=0 root=/dev/vda rw mem=128M ip=192.168.7.2::192.168.7.1:255.255.255.0 oprofile.timer=1 " | ubik@sentry:~/yoctoproject/build$ sudo kvm -kernel /home/ubik/yoctoproject/build/tmp/deploy/images/bzImage-qemux86.bin -net nic,model=virtio -net \ | ||
tap,vlan=0,ifname=tap0,script=no,downscript=no,vhost=on -drive file=/home/ubik/yoctoproject/build/tmp/deploy/images/core-image-core-qemux86.ext3,if=virtio \ | |||
-show-cursor -usb - usbdevice wacom-tablet -vga vmware -no-reboot -enable-kvm -cpu host -m 128 --append "vga=0 root=/dev/vda rw mem=128M \ | |||
ip=192.168.7.2::192.168.7.1:255.255.255.0 oprofile.timer=1 " | |||
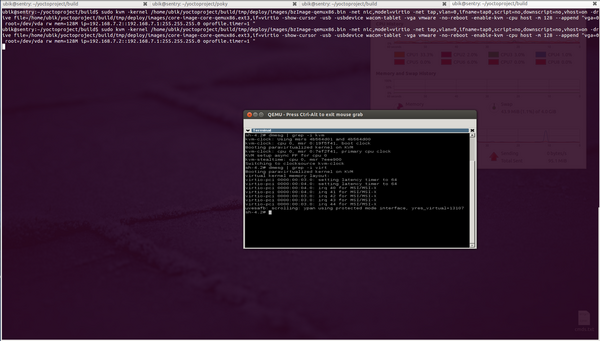
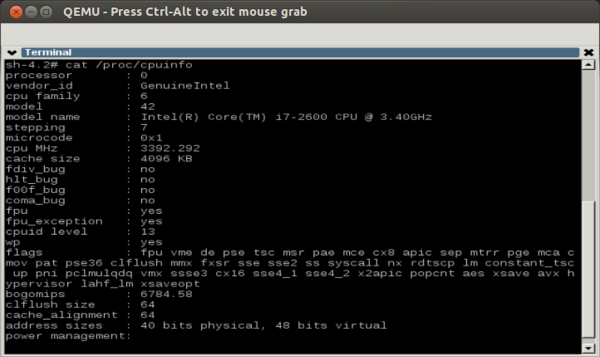
This is an example of running a virtualized Yocto image, with KVM active, cpu host features exported in the Yocto VM, paravirtualization enabled, and using virtio interfaces for disk access and networking. | This is an example of running a virtualized Yocto image, with KVM active, cpu host features exported in the Yocto VM, paravirtualization enabled, and using virtio interfaces for disk access and networking. | ||
On | On a machine equipped with a Core i7 2600 (3.4GHz, 4 cores, 8 threads)/8 GB RAM/Intel SSD G3 120GB qemux86 Yocto Linux boots in around 7 seconds for a core-image-x11. The same image boots in 20 seconds without virtualization optimizations and feels slower in usage. | ||
See the following screenshots: | |||
[[File:Core-image-x11.png|thumb|upright=2|left|Yocto Linux guest running under QEMU KVM with paravirtualization and virtio tech.]] | |||
[[File:YL-guest-QEMU-cpu-host.png|thumb|upright=2|CPU host features exported to Yocto Linux guest.]] | |||
== Guest OS preparation == | == Guest OS preparation == | ||
The following kernel configs needs to be enabled: | The following kernel configs needs to be enabled for Yocto Linux guest OS: | ||
CONFIG_PARAVIRT_GUEST=y | [...] | ||
CONFIG_PARAVIRT_GUEST=y | |||
CONFIG_KVM_CLOCK=y | |||
CONFIG_KVM_CLOCK=y | CONFIG_KVM_GUEST=y | ||
CONFIG_KVM_GUEST=y | CONFIG_PARAVIRT=y | ||
CONFIG_PARAVIRT_CLOCK=y | |||
CONFIG_PARAVIRT=y | CONFIG_VIRTIO_MMIO=y | ||
[..] | |||
CONFIG_PARAVIRT_CLOCK=y | |||
CONFIG_VIRTIO_MMIO=y | |||
Revision as of 09:16, 7 September 2012
Host OS preparation (VM manager host OS)
1.Enable KVM on the host machine
2. Enable on host OS vhost-net virtio networking accelerator to mitigate overhead on QEMU virtualization environment.
Load vhost-net module on KVM Host.
[root@dlp ~]#modprobe vhost_net [root@dlp ~]#lsmod | grep vhost
The result of running the commands should be similar to the following:
vhost_net 24241 0 macvtap 7867 1 vhost_net tun16825 3 vhost_net
Basically, follow the same guide as for enabling KVM on the host (step 1.), but replace kvm with vhost_net
3. Start the VM using the line below:
ubik@sentry:~/yoctoproject/build$ sudo kvm -kernel /home/ubik/yoctoproject/build/tmp/deploy/images/bzImage-qemux86.bin -net nic,model=virtio -net \
tap,vlan=0,ifname=tap0,script=no,downscript=no,vhost=on -drive file=/home/ubik/yoctoproject/build/tmp/deploy/images/core-image-core-qemux86.ext3,if=virtio \
-show-cursor -usb - usbdevice wacom-tablet -vga vmware -no-reboot -enable-kvm -cpu host -m 128 --append "vga=0 root=/dev/vda rw mem=128M \
ip=192.168.7.2::192.168.7.1:255.255.255.0 oprofile.timer=1 "
This is an example of running a virtualized Yocto image, with KVM active, cpu host features exported in the Yocto VM, paravirtualization enabled, and using virtio interfaces for disk access and networking. On a machine equipped with a Core i7 2600 (3.4GHz, 4 cores, 8 threads)/8 GB RAM/Intel SSD G3 120GB qemux86 Yocto Linux boots in around 7 seconds for a core-image-x11. The same image boots in 20 seconds without virtualization optimizations and feels slower in usage.
See the following screenshots:
Guest OS preparation
The following kernel configs needs to be enabled for Yocto Linux guest OS:
[...] CONFIG_PARAVIRT_GUEST=y CONFIG_KVM_CLOCK=y CONFIG_KVM_GUEST=y CONFIG_PARAVIRT=y CONFIG_PARAVIRT_CLOCK=y CONFIG_VIRTIO_MMIO=y [..]